

Occupational health and safety measures are taken at the company level through the employee’s personal information and advice about individual prevention. Occupational health care serves for the prevention and early detection of work-related illnesses, maintaining employability, and the further development of occupational health and safety.
The precautionary measures are defined in the appendices of the ArbMedVV. Accordingly, a distinction is made between mandatory, optional, and desired pension plans.
The employer must arrange this in the case of particularly hazardous activities. Participation is compulsory; employees are only allowed to work after engaging in the precautionary activity.
In the case of certain hazards, the employer must offer this option. However, the employees are not obliged to participate.
Employers must allow their employees, if they wish, to have regular occupational medical advice and examinations. This option does not exist if, based on the risk assessment and the protective measures taken, no damage to health is to be expected.
After each precautionary measure is taken, the certificates are issued to the employee and the employer. On the employer’s certificate, for confidentiality reasons, no statement on the employee’s health is listed. It only contains information about when and for what reason a check-up took place and when a follow-up appointment is scheduled.
The employer must keep the certificate in a precautionary file.
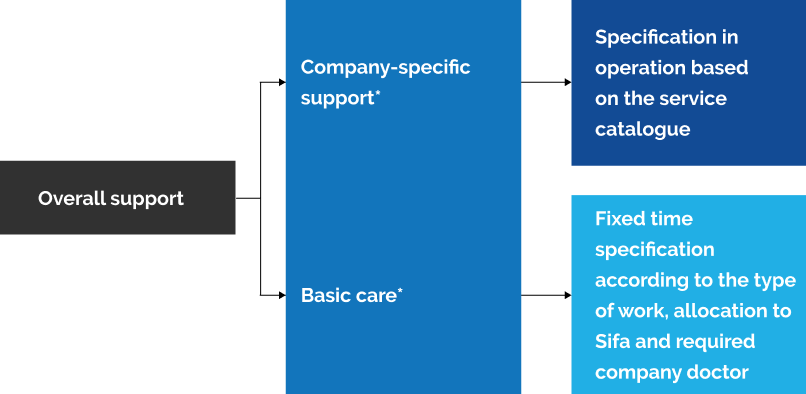
Tasks of basic support (in accordance with Annex 3 to Appendix 2, Section 2 of DGUV Regulation 2):
Tasks of company-specific support (in accordance with Annex 4 to Appendix 2, Section 3 of DGUV Regulation 2):

In Germany, there are a number of legal regulations that require a suitability test by law, for example:
The accident prevention regulations alone do not provide a sufficient basis. Therefore aptitude tests without cause are not permissible in the course of employment because they interfere with the employee’s right to privacy.
If required due to the activity, collective work agreements can be made. These agreements must take into account both the protection of the general public and the personal rights of the person under investigation. The principle of proportionality must always be observed. The consent of the employee to participate in these examinations is required. Aptitude examinations for specific reasons during an ongoing employment relationship can be permissible under certain conditions, for example:
• if there are justified doubts about the suitability of the employee. A reasonable doubt may arise from factual indications that point with sufficient certainty to a lack of suitability
• in the event of assignment to a new field of activity with a different requirement profile
We would be happy to advise you on this in a personal meeting with one of our specialists.
| Old | New | Examples activity areas |
|---|---|---|
| G20 | • Activities with exposure to noise
• Offered or obligatory precaution (according to defined trigger criteria) |
metalworking, construction sites, child care |
| G24 | • Activities within wet conditions
• Offered or obligatory precaution (according to defined trigger criteria) |
food processing, nursing and care for the elderly, doctors, hairdressers, dental technicians, cleaners |
| G37 | • Activities with display screen equipment
• Offered precaution |
office activity, sales/consulting |
| G42 | • Activities with risk of infection
• mandatory precaution (according to defined trigger criteria) |
nursing and care of the elderly, doctors, child care |

 Nord-EU AI Act
Nord-EU AI Act
 Empower Your Employees
Empower Your Employees
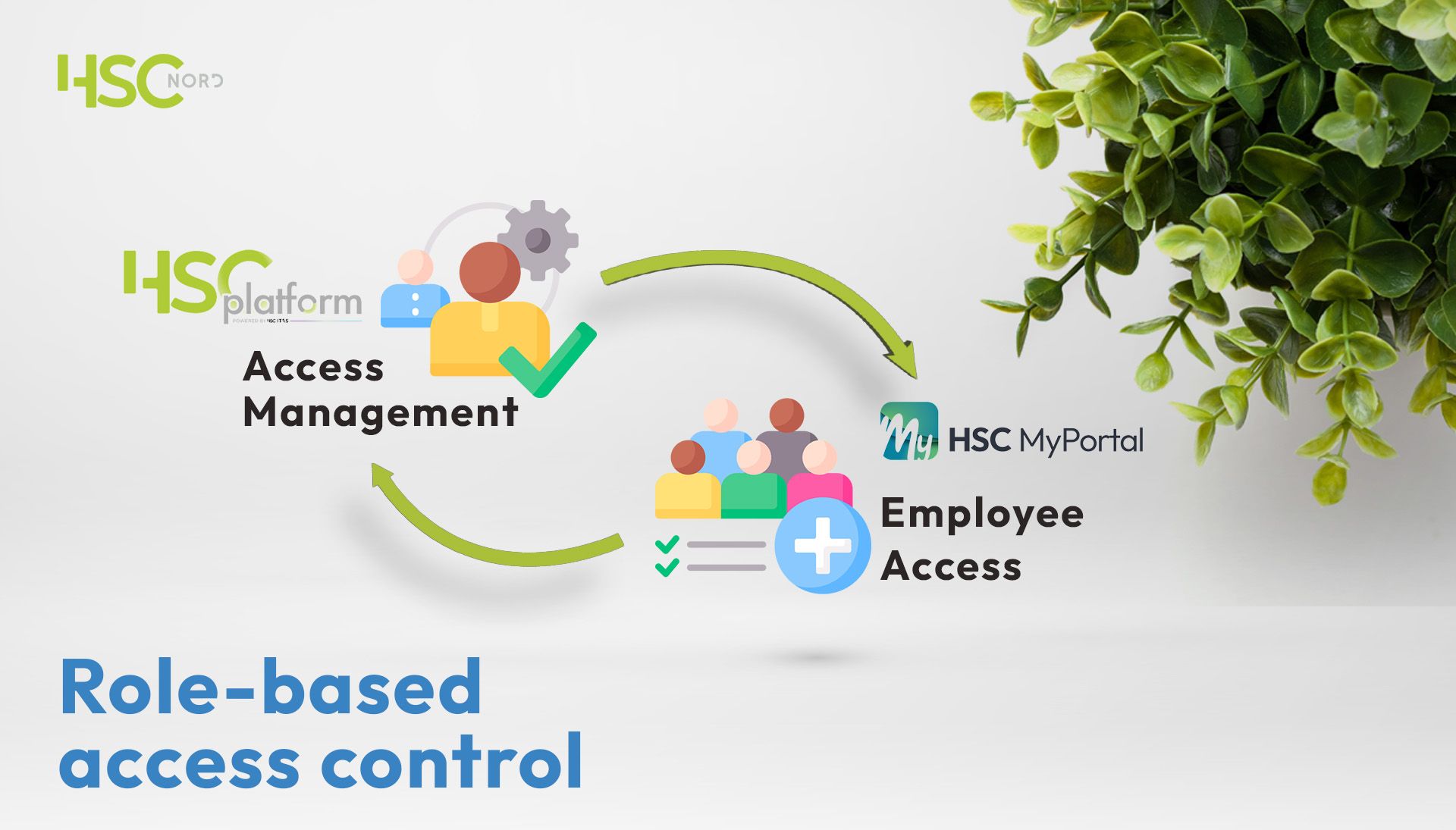 Role-based Access Control
Role-based Access Control